Tuesday, 3 May 2022
MCO-01 - ORGANISATION THEORY AND BEHAVIOUR - Masters of Commerce (Mcom) - First Semester 2022-2023
Sunday, 1 May 2022
Question No. 5 - MCO-06 - MARKETING MANAGEMENT - Master of Commerce (Mcom) 2nd Year
Solutions to Assignments
MCO-06 - MARKETING MANAGEMENT
Master of Commerce (Mcom) 2nd Year
Question No. 5.
Comment briefly on the following statement:
(a) Different phases of development in Indian market are indicators that there is a revolution undergoing in Indian market.
(b) Marketing research is quite pervasive in nature and can be used by the marketing managers in various marketing decision areas.
Even though research is performed to generate information, but managers will not readily use the information to solve their issues. The factors that influence a manager's decision to use research output are quality of research, conformity to prior expectations, presentation clarity, political acceptability within the firm, and challenge to the status quo. But make a note that researchers and managers agree that only the technical quality of research is the key determination of research use. Also, managers are less favourable to utilize research that does not conform to prior belief or is not politically acceptable. Some researchers state that the use of information and data is a function of the direct and indirect effects of environmental, informational, organizational, and individual factors. However, a researcher should not manipulate the findings to match a manager's prior belief. Further, managers in consumer firms are less likely to utilize research findings than their peer in industrial firms. This is due to a higher exploratory objective in data gathering, a greater interest of formal organizational structure, and a lesser interest of surprise in the data gathering. Ethics defines the moral principles or values that generally regulate the conduct of an individual or group.
Researchers have roles and responsibilities to their profession, respondents, and clients, and they must stick to high ethical standards to safeguard that both the function and the data are not brought into low esteem. The Marketing Research Association, Inc. (Chicago, Illinois) has established a code of ethics that gives as a guideline for ethical decisions making in marketing. Council of American Survey Research Organization (CASRO) has a detailed policy on marketing research ethics to which its members notice. Generally, Stakeholders involved in marketing research are
- Project client who sponsors
- Supplier who designs and executes the research
- Respondent who provides the information
In practice, a marketing research goal can be coupled into three major categories programmatic, selective, and evaluative. Where, Programmatic research is conducted to determine marketing opportunities through market segmentation, opportunity analysis, and consumer attitude and product usage research. Selective research is being done to test various decision alternatives such as new product testing, advertising testing, pre-test marketing, and test marketing. Evaluative research is performed to evaluate performance of programs such as tracking advertising recall, corporate and brand image research, and customer satisfaction measurement with the quality of the product and service. As increase in number of new products and types of services, the need for marketing research become vital and the future of marketing research tends to be both promising and challenging. Marking a new product is quite difficult. Companies are relentlessly working to get fresh information that identifies and explains the needs of new consumer segments. Some companies are stick their futures on product innovations, others are revitalizing. Not only the companies that always did marketing research doing well, the size of research activities also continues to increase.
- Researchers are doing more acquisition and competitor research, segmentation and market structure analysis, and basic strategic position assessments for senior management to support for its decisions.
- Other areas, such as the legal department use marketing research. Corporate Affairs needs to know shareholders, bankers, analysts, and employees attitudes and behaviour towards the company. The service department frequently audits service delivery capability and customer satisfaction.
- Whole industries that used to be protected from the unexpected and inexplicable change in and changing customer needs. Banks, Airlines, and financial services are seeing for ways to overcome advertising clutter, product proliferation, and high marketing costs brought on by sophisticated customers and competitors.
Human psychology is a major determinant of consumer behavior. These factors are difficult to measure but are powerful enough to influence a buying decision.
Some of the important psychological factors are:
i. Motivation
When a person is motivated enough, it influences the buying behavior of the person. A person has many needs such as social needs, basic needs, security needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization needs. Out of all these needs, the basic needs and security needs take a position above all other needs. Hence basic needs and security needs have the power to motivate a consumer to buy products and services.
ii. Perception
Consumer perception is a major factor that influences consumer behavior. Customer perception is a process where a customer collects information about a product and interprets the information to make a meaningful image of a particular product.
When a customer sees advertisements, promotions, customer reviews, social media feedback, etc. relating to a product, they develop an impression about the product. Hence consumer perception becomes a great influence on the buying decision of consumers.
iii. Learning
When a person buys a product, he/she gets to learn something more about the product. Learning comes over a period of time through experience. A consumer’s learning depends on skills and knowledge. While skill can be gained through practice, knowledge can be acquired only through experience.
Learning can be either conditional or cognitive. In conditional learning the consumer is exposed to a situation repeatedly, thereby making a consumer to develop a response towards it.
Whereas in cognitive learning, the consumer will apply his knowledge and skills to find satisfaction and a solution from the product that he buys.
iv. Attitudes and Beliefs
Consumers have certain attitudes and beliefs which influence the buying decisions of a consumer. Based on this attitude, the consumer behaves in a particular way towards a product. This attitude plays a significant role in defining the brand image of a product. Hence, marketers try hard to understand the attitude of a consumer to design their marketing campaigns.
(d) Marketing of services is no different from marketing of products, the strategies of the 4 P's, however, require some modifications when applied to services.
To understand the services marketing mix framework, it’s necessary to understand the nature of services. According to Wolak, Kalaftis & Harris, the characteristics of services are:
- Intangibility–the service cannot be touched or viewed, so it is difficult for clients to tell in advance what they will be getting.
- Inseparability (simultaneity)–the service is being produced at the same time that the client is receiving it (eg during an online search, or a legal consultation).
- Heterogeneity (variability)–services involve people, and people are all different. There is a strong possibility that the same enquiry would be answered slightly differently by different people (or even by the same person at different times). It is important to minimize the differences in performance (through training, standard-setting and quality assurance).
- Perishability–unused capacity cannot be stored for future use. For example, spare seats on one airplane cannot be transferred to the next flight, and query-free times at the reference desk cannot be saved up until there is a busy period.
Each of these characteristics plays a role in the service marketing mix.
The Services Marketing Mix
Extending the 4Ps
The services marketing mix is an extension of the 4Ps framework. The essential elements of product, promotion, price and place remain but three additional elements – people, physical evidence and process are included to the 7Ps mix. The need for the extension is due to the high degree of direct contact between service providers and its customers, the highly visible nature of the service process, and the simultaneity of the production and consumption. Although it is possible to discuss people, physical evidence and process within the 4P framework (for example, people can be considered part of the product offering), this extension allows for a more thorough analysis of the marketing elements necessary for successful services marketing.
Product
In the case of services, the “product” is intangible, heterogeneous and perishable. Moreover, its production and consumption are inseparable. Hence, there is scope for customizing the offering as per customer requirements, and the actual customer encounter therefore assumes particular significance. However, too much customization would compromise the standard delivery of the service and adversely affect its quality. Therefore, particular care has to be taken in designing the service offering.
Pricing
Pricing of services is tougher than pricing of goods. While the latter can be priced easily by taking into account the raw material costs, in the case of services there are attendant costs–such as labor and overhead costs–that also need to be factored in.
A restaurant not only has to charge for the cost of the food served but also has to calculate a price for the ambiance provided.
Place
Since service delivery is concurrent with its production and cannot be stored or transported, the location of the service product assumes importance. Service providers have to give special thought as to where the service is provided. A fine dining restaurant is better located in a busy, upscale market as opposed to the outskirts of a city. A holiday resort is better situated in the countryside away from the rush and noise of a city.
Promotion
Since a service offering can be easily replicated, promotion becomes crucial in differentiating a service offering in the mind of the consumer. Service providers offering identical services such as airlines or banks and insurance companies invest heavily in advertising their services. This is crucial in attracting customers in a segment where the services providers have nearly identical offerings.
People
People are a defining factor in a service delivery process, since a service is inseparable from the person providing it. A restaurant is known as much for its food as for the service provided by its staff. The same is true of banks and department stores. Consequently, customer service training for staff has become a top priority for many organizations today.
Process
The process of service delivery is crucial since it ensures that the same standard of service is repeatedly delivered to the customers. Most companies have a service blue print which provides the details of the service delivery process, often going down to even defining the service script and the greeting phrases to be used by the service staff.
Physical Evidence
Since services are intangible in nature, most service providers strive to incorporate certain tangible elements into their offering to enhance customer experience. Many hair salons have well designed waiting areas, often with magazines and plush sofas for patrons to read and relax while they await their turn. Similarly, restaurants invest heavily in their interior design and decorations to offer a tangible and unique experience to their guests.
Question No. 4 - MCO-06 - MARKETING MANAGEMENT - Master of Commerce (Mcom) 2nd Year
Solutions to Assignments
MCO-06 - MARKETING MANAGEMENT
Master of Commerce (Mcom) 2nd Year
Question No. 4.
Differentiate between the following:
(a) Product and Production concept of marketing
On the other hand, the production concept means that a brand or firm has to concentrate on products that can generate the most accurately. Low-cost products would produce by firms and it is believed that this cost will drive the demand for the product.
Product vs Production Concept
The main difference between Product and Production Concept is that the concept of the product is to create a good quality item/product which should be reliable along with unique features for the consumers. The concept of production is to make the product available in the market at an affordable price.
Comparison Table Between Product and Production Concept
| Parameter of Comparison | Product Concept | Production Concept |
|---|---|---|
| Preference of Consumers | Products that offer the best quality, performance, and creative specifications are preferred by consumers | Products that are broadly available and inexpensive are preferred by consumers |
| Meaning | Improvements in quality products | Easily accessible products |
| Business Goal | To enhance the quality of the product, creating new features, etc. | To enhance the quantity of production and to reduce the average cost. |
| Profit | Gets profit by providing a good quality product | Gets profit by expanding large scale production |
| Priority | Gives priority on the product | Gives priority on the production |
What is the Product Concept?
The meaning of Product Concept is that customers or consumers prefer a product that offers the best quality, performance, and features. In order to deliver the best possible product to the customer as per their requirement and expectation, this concept is a necessary one.
To achieve success, a product is not going to be complete by itself and it will need other factors such as- business-like marketing, delivery, sales, service, etc.
A firm or company can create an identity of the product and also can add practical value and advantages by using the Product concept. As a result, the expected customers can collect this benefit and sooner or later they will buy the product in the market.
Towards the market, the product concept is known as one of the orientations & marketing approaches that can be followed by a company.
The other strategies are Selling Concepts, Production Concepts, and Marketing Concepts, etc. Pull Marketing is created because of better products that provide aid in the success of the brand. And every creative innovation helps to get new products with features which will attract more customers.
For example, Apple is one of the companies that focuses extremely on their product concept to deliver the best products to their customers. Their products are considered to be of high quality with ingenious features and tremendous accomplishments. So, consumers want to purchase the products of Apple and that generates a pull marketing.
Therefore, this is the proper definition of the Product Concept along with its overview.
What is the Production Concept?
The production concept can be called a very effective organizational adjustment than any of the lists of other marketing concepts. It says the actual truth about how humans will prefer products that are inexpensive and can be easily found.
In the mid1950s this concept was discovered during the time of production era of early Capitalism. In that time, organizations concerned themselves principally with creation, assembling, and effectiveness issues.
Also, during this time, the ‘Says Law’ was developed with the idea of supply and demand. The actual thought behind this concept is that to maximize profitability and scale, businesses will always prefer to generate extensively cheap products in maximum volumes.
The owners of these businesses believe that customers are initially interested in product availability and low prices. In this way sometimes customer’s needs might not be fully addressed.
This kind of attempt is apparently most productive at the point when a business works in high development markets or where the potential for economies of scale is noteworthy.
Main Differences Between Product and Product Concepts
- In the product concept, even if the price of the product is high, a good quality product will sell itself. On the other hand, in the production concept, if the firm produces in bulk amount, the cost of production will be less, and so it will attract the customers for its low cost and will be easily sold.
- In the product concepts, consumers will always want the products that offer the most value in quality, performance, and innovative features. And in the production concepts, consumers will favor products that are available around them and are budget-friendly.
- The product concept can be followed by customers through the improvement in the product. Under other conditions, the production concept will be followed by upgrading the amount of product effectiveness and distribution coverage.
- The goal of the product concept is providing good quality rich products, with creative features and outstanding performance to the customers. And production concept targets at accomplishing economies of scale, through a major number of production and improving the supply chain.
- In a product concept, the product usually gets the utmost preference, and in the production concept, the production of goods will be given top priority.
- In the product concepts approach, the advancement of the product in terms of its features, performance, and quality are the means to achieve the end goals. In production concepts, maximizing projects, production should be done on a large scale which will make sure obvious availability and affordability of the product.
- A product concept is known as the thought for an item or product. And a production concept is known as the concept of conceiving to create the product.
- The production concept is useful for the companies when the demand for a product outruns the supply, and the cost of the product is too high. The product concept is nothing like that.
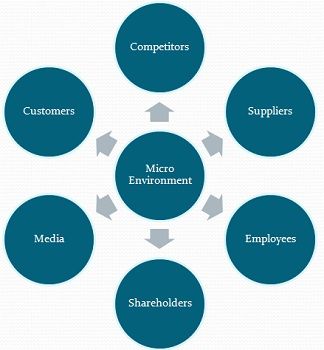
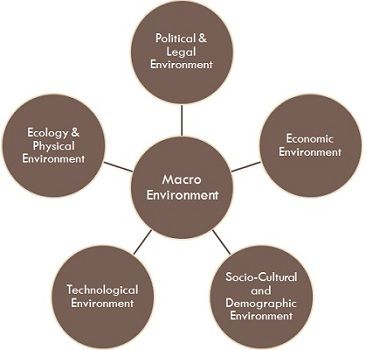
(b) Micro environment and Macro environment
 Every business organization is a part of the business environment, within which it operates. No entity can function in isolation because there are many factors that closely or distantly surrounds the business, which is known as a business environment. It is broadly classified into two categories, i.e. microenvironment, and macro environment. The former affects the working of a particular business only, to which they relate to, while the latter affects the functioning of all the business entities, operating in the economy.
Every business organization is a part of the business environment, within which it operates. No entity can function in isolation because there are many factors that closely or distantly surrounds the business, which is known as a business environment. It is broadly classified into two categories, i.e. microenvironment, and macro environment. The former affects the working of a particular business only, to which they relate to, while the latter affects the functioning of all the business entities, operating in the economy.
While microenvironment has a direct impact on business activities, the macro environment is a general business environment, which influences all business groups at large. It is important to learn the business environment, so as to understand the effect of various forces on business. Take a read of the given article to know the difference between microenvironment and macro environment.
Comparison Chart
| BASIS FOR COMPARISON | MICRO ENVIRONMENT | MACRO ENVIRONMENT |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Micro environment is defined as the nearby environment, under which the firm operates. | Macro environment refers to the general environment, that can affect the working of all business enterprises. |
| Elements | COSMIC, i.e. Competitors, Organization itself, Suppliers, Market, Intermediaries and Customers. | PESTLE, i.e. Political, Economic, Socio-cultural, Technological, Legal and Environmental. |
| Nature of elements | Specific | General |
| Are these factors controllable? | Yes, but to some extent only | No |
| Influence | Directly and Regularly | Indirectly and Distantly |
Definition of Micro Environment
Microenvironment refers to the environment which is in direct contact with the business organization and can affect the routine activities of business straight away. It is associated with a small area in which the firm functions.
The microenvironment is a collection of all the forces that are close to the firm. These forces are very particular for the said business only. They can influence the performance and day to day operations of the company, but for the short term only. Its elements include suppliers, competitors, marketing intermediaries, customers and the firm itself.
- Suppliers are the ones who provide inputs to the business like raw material, equipment and so on.
- Competitors are the rivals, which compete with the firm in the market and resources as well.
- Marketing intermediaries may include wholesalers, distributors, and retailers that make a link between the firm and the customers.
- Customers / Consumers are the ones who purchase the goods for their own consumption. They are considered as the king of business.
- The firm itself is an aggregate of a number of elements like owners like shareholders or investors, employees and the board of directors.
Definition of Macro Environment
The general environment within the economy that influences the working, performance, decision making and strategy of all business groups at the same time is known as Macro Environment. It is dynamic in nature. Therefore it keeps on changing.
It constitutes those outside forces that are not under the control of the firm but have a powerful impact on the firm’s functioning. It consists of individuals, groups, organizations, agencies and others with which the firm deals during the course of its business.
The study of Macro Environment is known as PESTLE Analysis. PESTLE stands for the variables that exist in the environment, i.e. Political, Economic, Socio-cultural, Technological, Legal and Environmental. These variables, consider both economic and non-economic factors like social concerns, government policies, family structure, population size, inflation, GDP aspects, income distribution, ethnic mix, political stability, taxes, and duties, etc.
(c) Market segmentation and Market targeting.
 In segmentation, the entire market of consumers is broken down into a number of groups. These groups are segments that comprise consumers with similar characteristics. Of all these segments the company chooses one segment to focus on, to offer their products. This is the process of targeting.
In segmentation, the entire market of consumers is broken down into a number of groups. These groups are segments that comprise consumers with similar characteristics. Of all these segments the company chooses one segment to focus on, to offer their products. This is the process of targeting.
We all know that, when all the consumers of the product are taken together, it makes up the market for that product. But this is also true all the consumers are not the same. Therefore, the consumers may differ in:
- Needs
- Motives
- Characteristics
- Buying habits.
With this, we can conclude that the market for the product is heterogeneous in nature. So, the marketers can divide the entire market into submarkets. These sub-markets are homogeneous.
Comparison Chart
| BASIS FOR COMPARISON | SEGMENTATION | TARGETING |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Segmentation is the process of classifying the market into several approachable groups. | Targeting is the process of concentrating on a particular segment of the market to offer products, of all the segments of the market. |
| Concerned with | Dividing up the market, by grouping the customers with similar needs. | Choosing the right segment considering different factors. |
| Bases | Need, Interest, Marital Status, Sex, Buying Behavior, etc. | Attractiveness of the segment |
| Stage of Target marketing | First | Second |
Definition of Segmentation
Segmentation implies splitting the heterogeneous market into relatively distinct homogeneous sub-market. To divide the market, specific criteria form the base.
These groups possess consumers, having common characteristics. The characteristics include age, income, sex, personality traits, or behavior. It aims at determining the consumer groups whose needs can be fulfilled with one common product. Above all, it ensures the concentration of the efforts of the firm in an effective and economical manner.
This helps in tapping the market in a better manner. Besides, it also helps in optimizing products and advertising them to consumer groups.
What is Market Segment?
Market Segment is that part of the entire market, wherein the consumers have one or more things in common. And due to this reason, their product needs are the same.
It is a strategic marketing tool. This is used to determine the market and also to allocate resources.
- All the buyers are not the same.
- Identification of consumers with similar characteristics. These can be background, need, values, behaviors, and so forth.
- There will be small sub-groups and often homogeneous in nature, as compared to the market.
- It is easier for the marketer to satisfy a small group with similar customers than a large group with diverse customers.
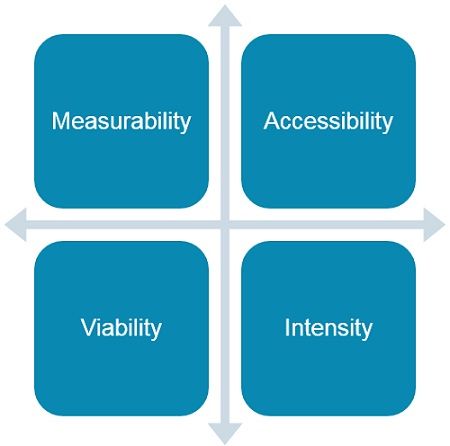
Requirements of Effective Segmentation
- Measurability: The segments have to be measurable. In other words, the quantification of the segment should be possible so that the size can be estimated.
- Accessibility: Segmentation should be done in a manner that the marketer may get through and serve the segments.
- Viability: Segments should be cost-effective as well as profitable to the marketer.
- Intensity: Attractiveness of segment is also ascertained by its intensity with regard to inter-firm rivalry. A higher intensity indicates more competition between firms. Therefore, it makes the segment unattractive for the marketer.
Definition of Targeting
After the creation of different segments, managers decide which segment is best to target. For the purpose of targeting the company takes into account its ultimate objectives. In practice, managers go for that segment that is highly profitable. But, the firm can also aim for that segment that is less likely to attract competitors.
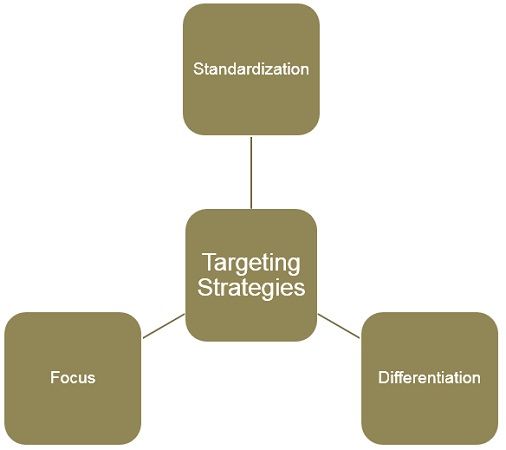
In other words, targeting is the process of choosing one segment, of all the segments, to aim for. There are three strategic options are available to the marketers which are:
- Concentrated Marketing: In this, the company focuses on a single segment at a time. Another term used for this is niche marketing. In this, the marketer attempts to become the blue-chip within that segment.
- Differentiated Marketing: In this strategy, the marketer concentrates on more than one segment at a time. Also, the company offers a differentiated marketing mix for each segment. The alternative name of this is multi-segmented marketing.
- Undifferentiated Marketing: In this, the marketer uses a ‘scattergun’ approach. Therefore, the marketers offer one basic product that would serve the needs of people belonging to different age groups and lifestyles.
The marketer’s decision about the adoption of strategy depends on these factors:
- Company’s Resources
- Product features and benefits
- Characteristics of the segment
Targeting Strategies
Standardization:
Here, the firm offers a similar product to different segments. For this, the same communication, distribution, and pricing strategy are used.
Differentiation:
In this, the company differentiates its products to match the needs and expectations of different segments of the market.
Focus:
It is a hybrid strategy. That is to say, it combines both standardization and differentiation strategies. Also, the ‘core strategy’ remains unchanged, but differentiation is implemented to fulfill the requirements of specific consumers.
(d) Captive Product Pricing and Product-Bundle Pricing
Captive Product Pricing
What Is Captive Product Pricing?
For instance, captive product pricing is a pricing strategy devised to attract a large volume of customers to a one-time purchase of a lower-priced core (or main) product that requires accessory (or captive) products for the main product to function. Consequently, companies might initially lose core product sales. For example, they may eventually enjoy increased revenue and sales through the recurring purchases of more expensive accessory products.
Therefore, this pricing strategy is one of five product mix pricing strategies. The other four include product line pricing, optional product pricing, by-product pricing, and product-bundle pricing.
Real-World Examples of the Pricing Strategy
Certainly, if you have a cell phone with a wireless plan, you’ve experienced the captive product pricing strategy firsthand. For example, the cell phone itself is the core product. Therefore, the phone’s wireless plan is the captive product. Similarly, other captive products include phone cases, earbuds, and other products created to increase functionality. Above all the goal is to encourage the use of the core product. Moreover, organizations feel the need to keep customers engaged with new products.
What is price bundling?
Price bundling (product bundling or product-bundle pricing) is a marketing strategy that combines two or more products to sell them at a lower price than if the same products were sold individually. The bundle pricing technique is popular in retail and eCommerce as it offers more value for the price. It can also help build customer loyalty and boost product sales.
Price bundling can be applied to any type of product, but it works best when there are two or more items in the bundle. For example, say you own an ice cream shop and want to offer customers deals on their favorite flavors. You could offer a bundle of three ice cream cones for $4 instead of selling them each at $1 each.
Common bundle pricing examples
Bundle pricing examples can be seen in many industries. The strategy is used to entice potential customers to purchase additional products or services that companies know will be valuable. You’ve likely seen the following real-life bundle pricing examples:
- Mobile devices sold with a data plan
- Microsoft Office 365 and G Suite
- Soup, salad, and breadsticks
In each of these bundle pricing examples, the customer is able to purchase everything they need at a single price, whether it’s software tools or dinner. The company selling these products provides more value in a single purchase than if each item in the product bundle were purchased separately. Think about it: your phone would be less useful without a data plan, and breadsticks really tie a meal together.
We’ve even seen successful subscription ecommerce retailers like Dollar Shave Club implement this bundle pricing strategy for their own products.
Thursday, 28 April 2022
Question No 3 - MCO-06 - MARKETING MANAGEMENT - Master of Commerce (Mcom) 2nd Year
Solutions to Assignments
MCO-06 - MARKETING MANAGEMENT
Master of Commerce (Mcom) 2nd Year
Question No. 3.
Write short notes on the following:
(a) Buying Behaviour Situations
Stages of the Consumer Buying Process
Six Stages to the Consumer Buying Decision Process (For complex decisions). Actual purchasing is only one stage of the process. Not all decision processes lead to a purchase. All consumer decisions do not always include all 6 stages, determined by the degree of complexity...discussed next.The 6 stages are:
- Problem Recognition(awareness of need)--difference between the desired state and the actual condition. Deficit in assortment of products. Hunger--Food. Hunger stimulates your need to eat.
Can be stimulated by the marketer through product information--did not know you were deficient? I.E., see a commercial for a new pair of shoes, stimulates your recognition that you need a new pair of shoes. - Information search--
- Internal search, memory.
- External search if you need more information. Friends and relatives (word of mouth). Marketer dominated sources; comparison shopping; public sources etc.
Hungry, want to go out and eat, evoked set is
- chinese food
- indian food
- burger king
- klondike kates etc
- Evaluation of Alternatives--need to establish criteria for evaluation, features the buyer wants or does not want. Rank/weight alternatives or resume search. May decide that you want to eat something spicy, indian gets highest rank etc.
If not satisfied with your choice then return to the search phase. Can you think of another restaurant? Look in the yellow pages etc. Information from different sources may be treated differently. Marketers try to influence by "framing" alternatives. - Purchase decision--Choose buying alternative, includes product, package, store, method of purchase etc.
- Purchase--May differ from decision, time lapse between 4 & 5, product availability.
- Post-Purchase Evaluation--outcome: Satisfaction or Dissatisfaction. Cognitive Dissonance, have you made the right decision. This can be reduced by warranties, after sales communication etc.
After eating an indian meal, may think that really you wanted a chinese meal instead.
(b) Mass Marketing
(c) Internet marketing
(d) Functional Middlemen
- They provide valuable information and feedback to producers about consumer behavior, changing tastes and fashions, upcoming rival businesses, etc.
- They enable manufacturers to concentrate on the primary function of production by handling the ancillary functions of warehousing, distribution, advertising, insurance, etc. They promote the goods to the consumers on behalf of the producers.
- Middlemen like banks and other financial institutions render financial services to manufacturers.
- They make the goods and services available to consumers at the right place, at the right time, and in the right quantity.
- Buyers and sellers are often unwilling to assume the market risk for fear of a possible loss. It is the middlemen in the process chain who assume the risks of theft, perishability, and other potential hazards.
Fundamentals of Stock Trading - Important Question/Answers for Examination
Fundamentals of Stock Trading Important Question/Answers for Examination Question 1 Explain the term investment and factors affecting inve...
-
IGNOU ASSIGNMENT SOLUTIONS MASTER OF COMMERCE (MCOM - SEMESTER 2) MCO-22- QUANTITATIVE ...
-
The Rattrap – Chapter Summary with Key Points Author: Selma Lagerlöf Book: Flamingo (Class 12 English) Theme: Human Kindness and Redemption ...
-
The Lost Spring – Chapter Summary with Key Points Introduction "Lost Spring: Stories of Stolen Childhood" is an insightful and mo...